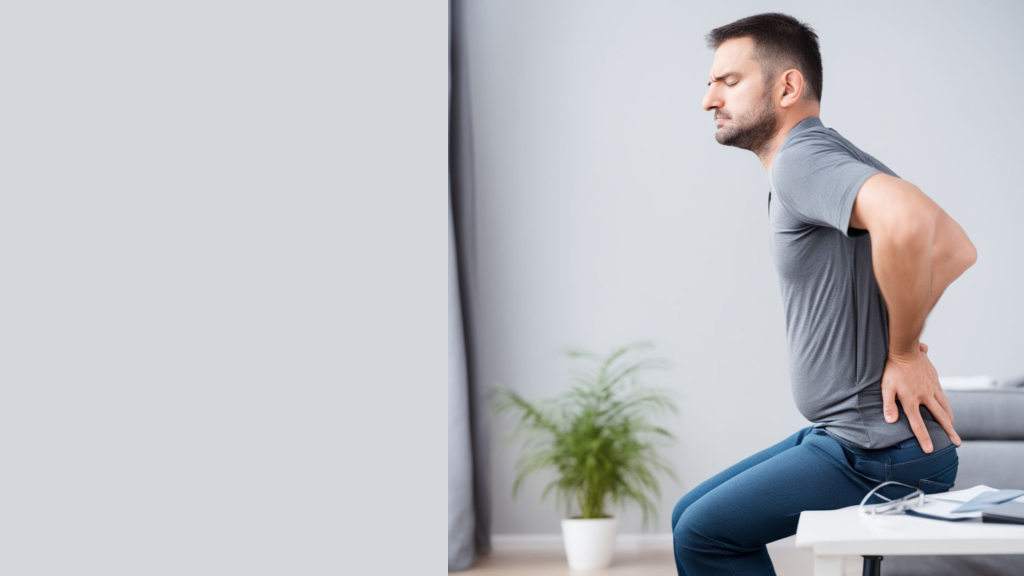
Addressing the enigma of lower lumbar discomfort proves to be an exceedingly formidable trial. If you’ve ever grappled with this affliction, you’re keenly aware of its tormenting and incapacitating essence, as well as its propensity to encroach upon your quotidian existence when it strikes. Furthermore, should you have encountered a lumbar infirmity, you apprehend that even after the initial anguish wanes, the specter of future lower back distress perpetually hovers.
Table of Contents
1) Lower Back Pain due to Muscle Spasms

Muscular spasms, also denoted as myotonic contractions, entail involuntary constrictions of one or more musculature components. A multitude of catalysts can incite these spasms, encompassing desiccation, excessive exertion, and underlying pathological maladies. Within the lower dorsal realm, these spasmodic occurrences can materialize as particularly excruciating and disruptive episodes.
Causes of Lower Back Muscle Spasms
- Overexertion and Strain: Inordinate tension or supererogatory exertion emerges as one of the chief instigating factors behind myotonic contractions in the lumbar region. This frequently arises during the act of hoisting ponderous objects or partaking in physically demanding endeavors.
- Dehydration: Inadequate fluid intake can give rise to the onset of myotonic contractions, and the musculature in the lower dorsum is no exception to this predilection. Dehydration can serve as a plausible catalyst for these spasms in this precise vicinity.
- Poor Posture: Maintaining a suboptimal bodily posture over a protracted interval places gratuitous duress upon the musculature in the lower back, thereby establishing the groundwork for myotonic contractions.
- Medical Conditions: Subterranean medical afflictions, such as intervertebral herniations or spinal stenosis, may also conduce to the manifestation of myotonic contractions in the lower lumbar domain.
Recognizing the Symptoms
How to Identify Lower Back Muscle Spasms
- Sudden Pain: Myotonic contractions frequently culminate in unforeseen and intense agony in the lower lumbar region. This distress can be incapacitating, rendering movement a daunting endeavor.
- Muscle Tightness: You may notice that the affected muscles become noticeably tight and knotted during a spasm.
- Limited Range of Motion: Muscle spasms can limit your ability to bend, twist, or move comfortably.
Watch the video demonstration and Get the Best Solution to relieve your problem
2) Lumbar Disc Prolapse
Lumbar disc prolapse is one common cause of lower back pain. It occurs when the discs that cushion and support the lumbar spine in your back become compressed, resulting in a loss of height or a slipped disc. Herniated discs are another main cause of lower back pain, but they are more uncommon. A herniated disc occurs when there is an issue with pressure and spinal nerves that can happen during everyday activities such as lifting something heavy or bending over.
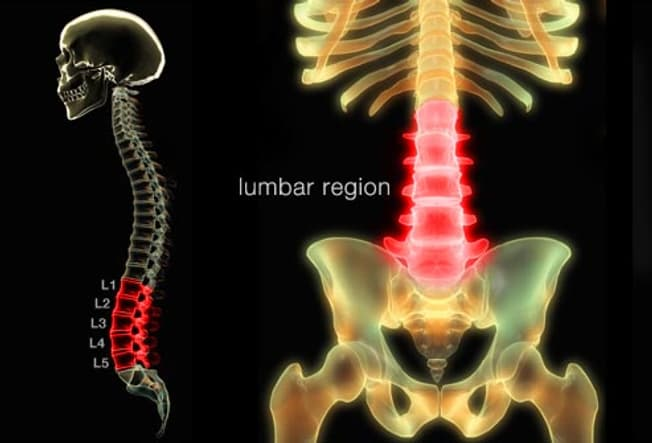
Lumbar Disc Prolapse, often referred to as a “slipped disc” or “herniated disc,” is a medical condition that primarily affects the lumbar region of the spine. Amidst this scenario, the pliable, gelatinous core, referred to as the nucleus pulposus, nestled between the vertebrae within the lumbar region, undergoes expansion or rupture by breaching the resilient, fibrous external layer, known as the annulus fibrosus. This phenomenon can be ascribed to a multitude of factors, including the inexorable effects of the natural aging process, the gradual attrition of the intervertebral structure, or an abrupt physical trauma.
When the nucleus pulposus protrudes through the annulus fibrosus, it applies pressure on nearby spinal nerves, leading to discomfort, pain, and occasionally, neurological symptoms. These manifestations might encompass localized lower back pain, the radiation of pain along one or both lower extremities (sciatica), paresthesia, tingling sensations, and muscular enfeeblement.
The gravity of lumbar disc prolapse can fluctuate, with certain individuals enduring mild unease, while others grapple with more acute indications that disrupt their daily routines. The spectrum of treatments for lumbar disc prolapse encompasses conservative methodologies such as rest, physical rehabilitation, and pain mitigation. In instances of heightened severity, surgical intervention may be necessary to either extract or rectify the compromised disc. The choice of treatment depends on the individual’s specific condition and the recommendations of a healthcare professional.
3) Tumors
There exist numerous potential origins for back discomfort, yet the most prevalent among them are tumors. A myriad of tumor varieties, including nerve neoplasms, tumor metastases, and even benign growths, hold the capacity to incite back pain. If you suspect that a tumor might underlie your back distress, it is of paramount importance to promptly pursue a medical examination. After conferring with a medical expert, you will probably undergo diagnostic radiographic examinations, such as X-rays or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), to unveil the underlying origin.
4) Degenerative arthritis
Individuals grappling with degenerative arthropathy confront an augmented susceptibility to lower lumbar aches, particularly those who actively partake in routine physical pursuits. Regrettably, this malady commonly evades a panacea, and its manifestations can be profoundly incapacitating. Unfortunately, this ailment typically lacks a cure, and its symptoms can be profoundly debilitating. While there is no recognized remedy for degenerative arthritis, the following therapeutic modalities are frequently employed to mitigate and forestall discomfort: pharmaceutical intervention, application of cold compresses, utilization of heat therapy, and engagement in massage therapy.

One surprising thing you can do in bed is to help you stay pain-free all day long.
5) Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis, a condition primarily afflicting the elderly, is characterized by a decline in bone density and increased fragility. Its principal culprits are insufficient physical activity and a diet lacking in protein. Fortunately, there exist methods to prevent or address this issue: ensuring an adequate protein intake, engaging in regular exercise, and fortifying your core can prove highly effective in alleviating back discomfort. Dedicate twenty minutes, twice daily, to yoga stretches to alleviate back pain concerns.
6) Infections
A prevalent instigator of lower lumbar agony is infection. An infected spinal disc has the potential to compress and provoke irritation in a spinal nerve, leading to intense back pain, tingling or numbness in the legs, or sharp, shooting sensations radiating from the buttocks down one leg. You may also encounter fever and chills. Should any redness or swelling manifest around the injury site, it is imperative to promptly consult a medical professional.
The tiny muscle is the #1 cause of back pain.
7) Chronic stress/anxiety
Back pain is an ever-present concern that affects people from all walks of life. While well-recognized causes such as muscle strain or structural spinal issues are common, one often underestimated yet significant contributor to back pain is chronic stress and anxiety.
The Mind-Body Connection
The intricate and potent connection between the mind and the body comes into play here. When we endure persistent stress or anxiety, our bodies initiate a sequence of intricate physiological transformations. This encompasses the release of stress hormones such as cortisol, which, when consistently elevated, can result in a spectrum of physical manifestations, including back pain.
Muscular Tension
Persistent stress and anxiety can manifest as muscular tension within the body. During periods of stress or anxiety, muscles often contract and tighten. This reflexive response can be beneficial in the short run, readying the body for a “fight or flight” reaction. However, when stress becomes a chronic companion, the muscles persist in a perpetual state of tension. In the context of the back, this tension can give rise to pain and discomfort.
Check Our Blog: 5 Healthy Lifestyle Tips You Need to Know
Posture and Movement
Persistent stress and anxiety can manifest as muscular tension within the body. During periods of stress or anxiety, muscles often contract and tighten. This reflexive response can be beneficial in the short run, readying the body for a “fight or flight” reaction. However, when stress becomes a chronic companion, the muscles persist in a perpetual state of tension. In the context of the back, this tension can give rise to pain and discomfort.
Central Nervous System Sensitization
Chronic stress and anxiety can heighten the sensitivity of the central nervous system. This means it becomes more receptive to pain signals. Consequently, even minor issues in the back, which might typically be painless, can become sources of discomfort when stress or anxiety looms.
Coping Mechanisms
Those grappling with chronic stress or anxiety may also develop coping mechanisms that inadvertently contribute to back pain. For instance, some individuals may turn to emotional eating or become less physically active, potentially leading to weight gain and back strain.
Breaking the Cycle
Recognizing the correlation between chronic stress and back pain is the initial step in addressing this issue. Managing stress and anxiety through methods like relaxation, mindfulness, or even seeking professional assistance through therapy can prove effective in alleviating back pain. Furthermore, maintaining regular physical activity and practicing good posture can help mitigate the physical toll of chronic stress on the back.

Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the seven main causes of lower back pain is crucial for effectively addressing and relieving this common ailment. Whether it’s muscle strain, herniated discs, poor posture, or any of the other causes discussed, the key to relief lies in a combination of prevention and targeted treatments. By maintaining a healthy lifestyle, practicing good posture, and seeking professional guidance, when necessary, individuals can take proactive steps to alleviate lower back pain and enjoy a more comfortable and pain-free life. There’s no definitive evidence that special shoes, shoe inserts, back supports, specially designed furniture, or stress management programs help to prevent or relieve back pain.
Furthermore, it’s important to note that not all mattresses are perceived as equal by those dealing with back pain. The ideal choice may ultimately be the one that provides the utmost comfort to you.
FAQ
Q1: What are the common causes of lower back pain?
The article discusses seven main causes of lower back pain, which include factors such as poor posture, muscle strain, herniated discs, and more. It provides detailed insights into each of these causes.
Q2: How can I relieve lower back pain at home?
The article offers practical tips and strategies for relieving lower back pain, including exercises, stretches, and lifestyle adjustments that you can implement on your own.
Q3: Is lower back pain a sign of a serious medical condition?
The article addresses this concern by explaining that while lower back pain is often due to common causes, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional if the pain is severe, persistent, or accompanied by other worrisome symptoms.
Q4: Are there preventative measures to avoid lower back pain?
Yes, the article discusses preventive measures and habits you can adopt to reduce the risk of lower back pain, such as maintaining good posture, exercising regularly, and ergonomically optimizing your workspace.
Q5: Are there specific exercises mentioned in the article to help with lower back pain?
Yes, the article provides a selection of exercises and stretches specifically designed to alleviate lower back pain. These are explained in detail and accompanied by instructions and illustrations.
Q6: Can I use over-the-counter medications for lower back pain relief?
The article covers various pain relief options, including over-the-counter medications, but advises on the importance of consulting with a healthcare professional before using any medication to ensure it’s safe and suitable for your specific situation.
Q7: What is the significance of understanding the causes of lower back pain?
Understanding the causes of lower back pain is crucial for making informed choices regarding its treatment and prevention. The article delves into why knowing the causes is essential for effective management.
Q8: How long does it typically take to relieve lower back pain using the methods discussed in the article?
The article provides insights into the expected timelines for relief using the recommended methods, though it’s important to note that individual experiences may vary.
Q9: Is surgery a common solution for lower back pain, and is it discussed in the article?
The article briefly discusses surgical options for severe cases of lower back pain but emphasizes that surgery is usually considered only after non-surgical treatments have been exhausted.
Q10: Where can I find more information on the topic of lower back pain and its relief?
The article may provide additional resources, references, or links to reputable sources where you can further explore the topic of lower back pain, its causes, and relief methods.








