- Whooping cough (pertussis) cases are spreading in Brown County, Wisconsin.
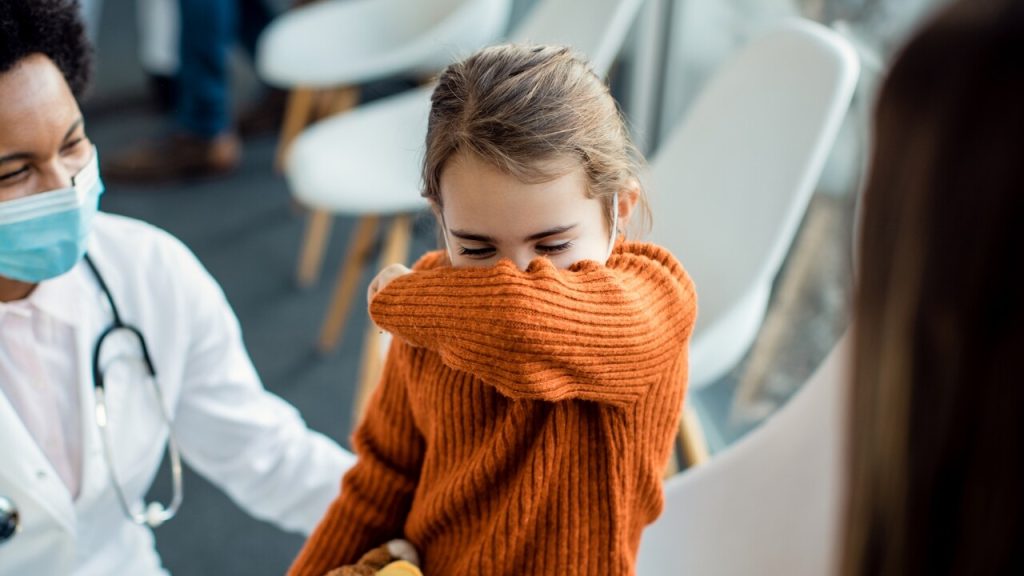
- Symptoms include runny nose, sneezing, cough, fever, and later violent coughing fits.
- Vaccination (DTaP/TDaP) is the best way to prevent infection.
Public health officials in Brown County are issuing a warning to residents as cases of whooping cough, also known as pertussis, continue to spread within the community. This announcement follows a recent memo sent to parents and staff at De Pere High School, where “probable” cases of whooping cough were identified. Whooping cough is a highly contagious respiratory disease that can be transmitted through coughing, sneezing, or close contact.
Whooping Cough Cases Spreading in Brown County
Health officials are concerned about the increasing spread of whooping cough in Brown County. The disease can be spread easily from person to person, especially in close-knit communities like schools and workplaces. It’s important for residents to be aware of the symptoms and take preventive measures to avoid contracting or spreading the disease.
Early Symptoms of Whooping Cough
Initial symptoms of whooping cough are similar to those of a common cold and include a runny nose, sneezing, occasional cough, and a low-grade fever. However, the disease can progress rapidly, leading to more severe symptoms if left untreated.
As whooping cough progresses, it can cause fits of violent coughing, followed by a deep breath that produces a “whooping” sound. This can make breathing difficult and may lead to vomiting and exhaustion.
While whooping cough can affect people of all ages, it poses a significant risk to infants, especially those under one year old. Infants are often infected by family members, caregivers, or older siblings who may not realize they are carrying the disease.
Health officials emphasize the importance of vaccination as the best way to prevent whooping cough. Vaccines such as DTaP for young children and Tdap for teens and adults are highly effective in protecting against Diphtheria, Tetanus, and Pertussis.
If you or your child develop symptoms of whooping cough, or if you have been exposed to someone with the disease, it’s important to take precautions. Stay home from school, work, or other activities to prevent further spread, and seek medical attention promptly to receive appropriate treatment.
Early treatment with antibiotics can help reduce the severity of whooping cough and prevent its spread to others. It’s crucial to consult a healthcare provider if you suspect you have been exposed to or are experiencing symptoms of whooping cough.
The recent increase in whooping cough cases in Brown County highlights the importance of vaccination and early detection. Public health officials urge residents to stay informed about the disease and take necessary precautions to protect themselves and their communities. By following preventive measures and seeking prompt medical attention, we can help contain the spread of whooping cough in our area.
Tags: whooping cough, pertussis, Brown County outbreak, public health alert, contagious respiratory disease, vaccination, symptoms, prevention, community spread, infant risk, Whooping cough cases, Brown County, whooping cough spreading, whooping cough outbreak, public health officials, Henderson County
FAQs
What is whooping cough?
Whooping cough, or pertussis, is a highly contagious respiratory disease caused by the bacterium Bordetella pertussis.
How is whooping cough spread?
Whooping cough is spread through respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes.
Who is at risk for whooping cough?
People of all ages can get whooping cough, but it is most severe in infants under one year old.
What are the symptoms of whooping cough?
Early symptoms include a runny nose, sneezing, and a mild cough, which can progress to severe coughing fits.
How is whooping cough treated?
Treatment typically involves antibiotics to reduce the severity of symptoms and prevent spread to others.
How can whooping cough be prevented?
Vaccination is the most effective way to prevent whooping cough. Regular handwashing and avoiding close contact with infected individuals can also help prevent its spread.